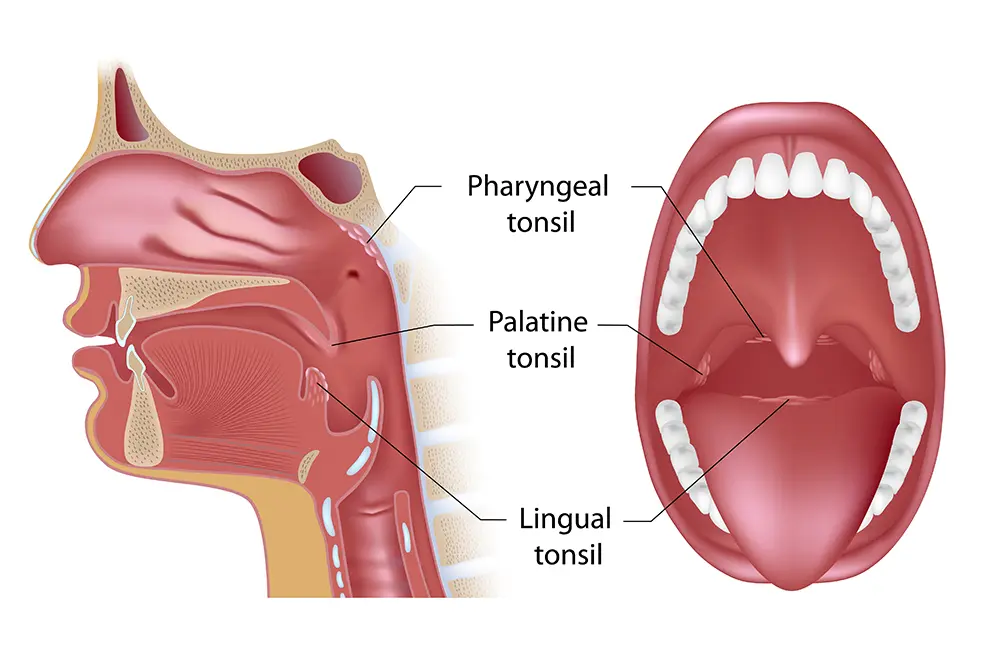
What Are Tonsils?
Your palatine tonsils form a protective ring around the back of your throat and act as your body’s first line of defense against viruses, bacteria, and germs that enter the mouth. These two, small, oval-shaped glands are a part of your body’s immune system housing white blood cells that help you fight off infections. Unfortunately, they can become infected themselves (tonsillitis), and if you find yourself with recurring episodes of tonsillitis, you may benefit from a tonsillectomy.

What Is a Tonsillectomy and Why Is It Performed?
This is a common surgical procedure that removes the palatine tonsils from the back of your throat. It is performed to treat infection and inflammation of the tonsils in individuals who have chronic or severe episodes of tonsillitis. A tonsillectomy is also used to treat complications from enlarged tonsils, such as difficulty swallowing or obstructive sleep apnea. It may also be used to treat rare diseases or conditions that affect the tonsils like cancer, tonsil stones, or halitosis related to the tonsils’ crevices.
What Is Tonsillitis & When Does a Tonsillectomy Benefit Sufferers?
This is an infection of the tonsils at the back of the throat. It is often accompanied by swelling, a sore throat, fever, trouble swallowing, and sometimes swollen lymph nodes in the neck. Your tonsils may become covered with a white or yellow coating, and your throat may be sore and red. Antibiotics are usually the first line of treatment. A tonsillectomy may be beneficial if:
- You have had 7 episodes of tonsillitis in the last 12 months.
- You have had at least 5+ episodes in the past 24 months.
- You have had at least 3 episodes a year in the past 36 months.
A tonsillectomy is also the recommended course of action if antibiotic treatment does not improve the bacterial infection causing the tonsillitis. If the infection results in frequent peritonsillar abscess, which may not improve with medication or drainage, then a tonsillectomy is the next step.
How To Prepare for a Tonsillectomy Procedure
Our ENT physicians ask that you stop taking anti-inflammatory and anticoagulant medications one week prior to your surgery, as these increase the risk of post-operative bleeding. We also ask that you do not eat or drink after midnight on the night prior to your procedure, as this will prevent anesthesia complications. Finally, we ask that you have a responsible adult with you for a ride home as well as for aftercare for at least 24 hours after surgery. Recovery from tonsillectomy is may take up to two weeks.
How Long Does the Procedure Take?
A tonsillectomy usually takes around 30-45-minutes and is done under general anesthesia. Our ENT physicians here at Florida Otolaryngology Group will take a detailed medical history and physical exam that assesses medicatoons, dietary supplements, and allergies, a family history of bleeding disorders, or negative reactions to antibiotics and anesthetics.
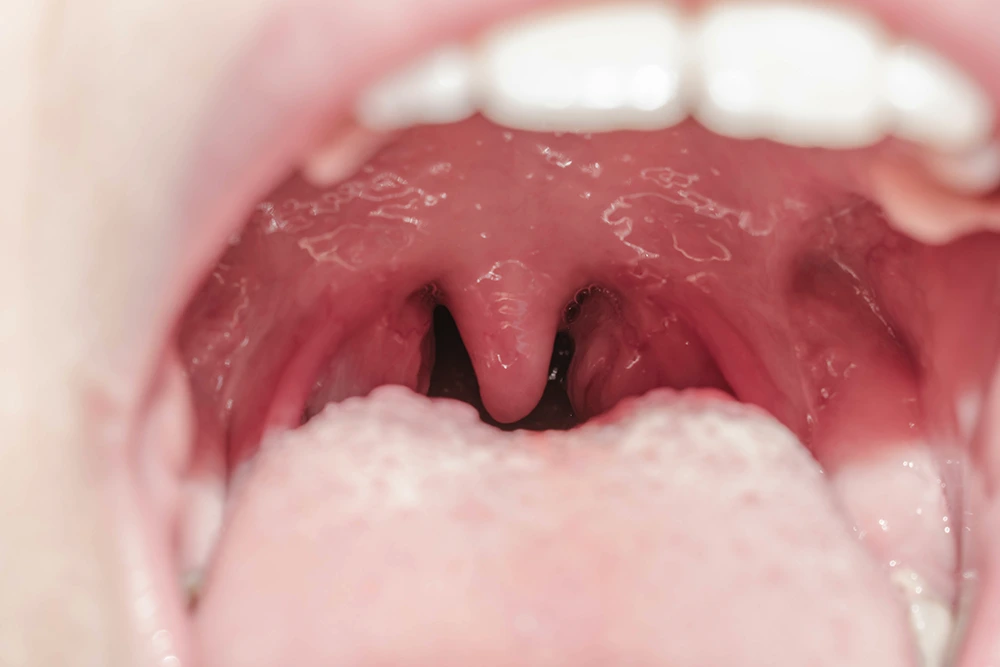
What Does Recovery Look Like After a Tonsillectomy?
You will experience pain during the healing process which will be treated with prescribed pain medication. Expect a sore throat, pain in the ears, neck, and jaw, as well as yellow discoloration where your tonsils were. This discoloration will look similar to a scab and will disappear a few weeks after the surgery.
It is important to eat soft foods during your recovery, such as popcicles, applesauce, broth, ice cream, and pudding. You want to avoid hard, spicy, or crunchy foods as these will cause pain or increase bleeding. Also it is important to avoid strenuous activities for the first 2-weeks and to get a lot of rest to help with the healing process.
Have Questions About the Tonsillectomy Procedure?
If you’d like to learn more about the benefits of tonsillectomies, our ENT physicians are happy to answer your questions or concerns. You can contact us here, or give us a call at: 407-677-0099. We serve the communities of Orlando, Winter Park, and Kissimmee.

Painful ear infections are a rite of passage for children—by the age of five, nearly every child has experienced at least one episode. Most ear infections either resolve on their own (viral) or are effectively treated by antibiotics (bacterial). But sometimes, ear infections and/or fluid in the middle ear may become a chronic problem leading to other issues such as hearing loss, behavior and speech problems. In these cases, insertion of an ear tube by an otolaryngologist (ear, nose and throat specialist) may be considered.


