Immittance Testing
Immittance Audiometry consists of three procedures: tympanometry, acoustic reflex testing and reflex decay testing. These tests measure alterations and fluctuations of the eardrum (tympanic membrane) and the integrity of the nervous system in response to stimuli. Information obtained from these procedures can offer insight into the pathologies of the middle ear. Immittance audiometry is used to determine the presence of middle ear fluid, Eustachian Tube dysfunction and the status of ventilation tubes after surgical insertion, as well as problems in the nerves between the ear and the brain.
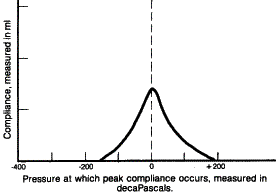
This is an example of an abnormal Right tympanogram. The absence of a peak indicates middle ear fluid.
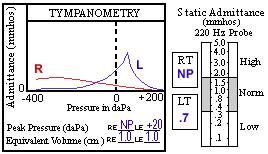
An example of a normal tympanogram.
Immittance Audiometry is Used For:
- Tympanometry, an objective test used to evaluate the movement of the eardrum and the status of the middle ear.
- Acoustic Reflex Test, a measurement of slight changes in the eardrum due to response from a pair of muscles in the middle ear to loud sounds.
- Reflex Decay Test, to determine whether hearing loss is related to the cochlea or the acoustic (Auditory) nerve, achieved by presenting a loud tone for 10 seconds while middle ear muscle contraction is monitored.